- Home
- Background
- ICIDOSE
- IDEAplus
- Newsletter
- IDEA
- Internal Dosimetry
- IDEAS Guidelines
- Structured approach
- NORM
- German
- Contact
Dose to the offspring
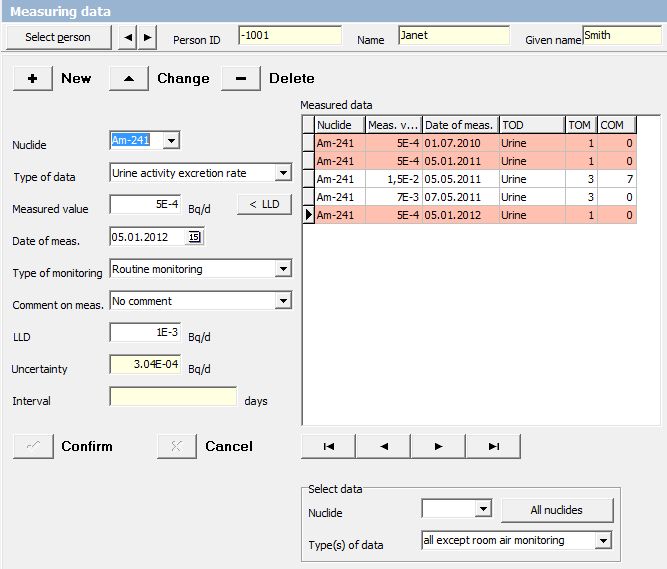
This hypothetical case study refers to a young women who was working with Am-241 some years ago for preparing her PhD thesis. Beginning on 01.01.2010 she was monitored by routine urinary excretion measurements with the monitoring interval being 180 d.
The first two routine measurements didn't show any findings. However, on the 03.05.2011 there was an incident with a significant release of Am-241 to the air. The room air monitoring results were available on 04.05.2011 and thus a urine sample was collected on the next day. This sample revealed a significant excretion of 15 mBq Am-241. A control measurement two days later confirmed that there was an intake of Am-241.
The evaluation of the measurements....
...revealed an intake of 71 Bq Am-241 resulting in a committed effective dose of 1.92 mSv with the highest exposed tissue being the bone surface with an organ dose of 78.1 mSv.
Recently the young woman got pregnant and she is very concerned because she remembers the intake of Am-241 five years ago. She knows that Am-241 is deposited in the bone with the effective half-life being 50 years and so she is afraid that there might be a risk for her baby because of the residual activity in her skeleton. Thus she has asked the radiation protection staff in her institute about the potential risk for her baby.
IDEA System can give an answer on this question according to ICRP Publication 88 with only few clicks as shown in the left screen-shot. You only have to enter the date of conception and the working period. The expert system will identify all intakes during this period and then calculate the dose to the offspring due to these intakes.
In this case the dose to the offspring would be in the order of 2 µSv (the calculated value is 2.37 µSv). Because of the uncertainties of the assessment model, however, this value is only a rough estimate of the real committed dose. Nevertheless this value is kind of best estimate, because it takes into account all information provided by the ICRP.
The limit of the dose to the offspring is 1 mSv and so in this case the dose would be far below the limit. Taking into account that the limit itself is far below the dose level where radiation induced effects such as mental retardation can be observed (about 100 mSv), there would be really no reason to be worried in this case.
This would be a good and helpful information for the young woman.